Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than once. a. | coalition | b. | political party | c. | major
parties | d. | minor party | e. | split-ticket voting | f. | precinct | g. | pluralistic
society |
|
|
|
1.
|
the smallest unit of election administration
|
|
|
2.
|
a group of people joined together on the basis of common principles, who seek
to control government and public policy
|
|
|
3.
|
consisting of several distinct cultures and groups
|
|
|
4.
|
the dominant political parties in the United States
|
|
|
5.
|
casting ballots for candidates from different parties for different offices in
the same election
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than once. a. | ward | b. | electorate | c. | minor
party | d. | plurality | e. | political party | f. | split-ticket
voting | g. | splinter parties | h. | major parties | i. | bipartisan |
|
|
|
6.
|
a unit into which cities are divided for the election of city council
members
|
|
|
7.
|
parties that have broken off from one of the major parties
|
|
|
8.
|
the greatest number of votes cast for a single office
|
|
|
9.
|
the people eligible to vote in any given election
|
|
|
10.
|
a group that seeks to control government by winning elections and holding
public office
|
|
|
11.
|
the two major parties acting together and cooperating when making
decisions
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | economic protest
parties | b. | consensus | c. | two-party system | d. | splinter
party | e. | one-party system | f. | minor party |
|
|
|
12.
|
Because the United States has a ____, the only candidates who have a reasonable
chance of winning an election are either Republicans or Democrats.
|
|
|
13.
|
Any party that has less support than one of the major political parties in the
United States is a(n) ____.
|
|
|
14.
|
Parties that want to express their discontent with the major parties and
current economy are known as ____.
|
|
|
15.
|
In dictatorships, the ____ could more realistically be called a
"no-party" system.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | precinct | b. | splinter
parties | c. | single-issue parties | d. | partisanship | e. | coalition |
|
|
|
16.
|
Congress and the State legislatures are often organized on party lines and
conduct much of their business based on ____.
|
|
|
17.
|
____ seek to cause a change on one public policy matter.
|
|
|
18.
|
A ____ is a union of many people of diverse interests who have joined
together.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
19.
|
In the United States, a political party is made up of a group of people
who
a. | disagree on how to resolve the basic issues affecting the
country. | b. | work to get candidates elected to political offices. | c. | work separately to
support one major program or policy. | d. | support split-ticket
voting. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Most single-issue parties have been
a. | short-lived. | b. | long-lived. | c. | rooted in times of
economic crisis. | d. | centered around a strong personality. |
|
|
|
21.
|
A multi-party system
a. | tends to produce a stable government. | b. | helps one party win the support of a majority
of voters. | c. | is composed of parties with special interests. | d. | promotes the
ideological consensus of the public. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which statement does NOT describe one type of minor party?
a. | The members of a minor party are united by a particular group of
viewpoints. | b. | A minor party is a party that has broken away from a major party. | c. | The members of a
minor party tend to support the platform of a major party. | d. | A minor party
expresses discontent over the state of the economy. |
|
|
|
23.
|
The national chairperson of a major political party
a. | organizes congressional campaigns. | b. | develops the platform upon which a presidential
candidate runs. | c. | manages the party's headquarters. | d. | elects all members of the national
committee. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Although United States political parties focus on winning elections, most
political parties in other countries also
a. | have certain principles they want adopted by government. | b. | seek to discourage
compromise. | c. | support the one-party system of government. | d. | all of the
above. |
|
|
|
25.
|
People belong to a particular political party
a. | according to regulations of State law. | b. | voluntarily, because they made a personal
choice. | c. | based on the location of the State in which they live. | d. | according to
regulations of federal law. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following statements about Federalists is TRUE?
a. | They called for a strict interpretation of the Constitution. | b. | George Washington
founded their party. | c. | They were generally supported by
farmers. | d. | A strong national government was of great concern to
them. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following is NOT a major function of either of the two major
parties in the United States?
a. | To keep the general public informed about key issues. | b. | To monitor the
conduct of its candidates in office. | c. | To assure the qualifications of candidates for
office. | d. | To unite people and concentrate solely on one public policy
matter. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Over time, the ideas first developed by minor parties are often ____ by major
parties.
a. | ignored | b. | borrowed | c. | suppressed | d. | attacked |
|
|
|
29.
|
The State party organizations
a. | are generally loosely tied to the national committee. | b. | face tight control
by the national committee. | c. | are well-disciplined
groups. | d. | always cooperate with one another. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is NOT one of the three main elements of the major
parties in terms of the roles of their members?
a. | the party organization | b. | the party in the electorate | c. | the party media
consultants | d. | the party in government |
|
|
|
31.
|
Parties that hold a particular set of beliefs and have often supported Marxist
thinking are known as
a. | ideological parties. | b. | single-issue parties. | c. | splinter
parties. | d. | economic protest parties. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Membership in either of the two major parties is
a. | closely regulated by federal law. | b. | closely regulated by State
law. | c. | based on economic status. | d. | based on personal
choice. |
|
|
|
33.
|
The two-party system developed in the United States mainly because
a. | the Constitution established a democratic government. | b. | conflicts about the
Constitution created opposing viewpoints. | c. | leaders and voters agreed on the existence of
two parties. | d. | it was voted on and approved by both houses of
Congress. |
|
|
|
34.
|
The era of one-party domination that began in 1968 was different from past eras
of one-party domination because
a. | the Republican party gained no new members in Congress. | b. | the Democratic party
gained no new members in Congress. | c. | one party controlled Congress while the other
controlled the presidency. | d. | minor parties interfered with the power of the
Republican party. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Minor parties have contributed MOST to United States politics by
a. | causing major parties to adopt their ideas. | b. | providing more
candidates from which voters can choose. | c. | placing their presidential candidates on the
ballot. | d. | establishing political precedents. |
|
|
|
36.
|
Which factor does NOT add to the decentralization of both major parties?
a. | Neither party has a chain of command at national, State, and local
levels. | b. | The government of the United States is a federal system. | c. | The process of
nominating candidates creates party conflict. | d. | The President heads one of the major
parties. |
|
|
|
37.
|
Which of the following is a sign of weakened political parties?
a. | split-ticket voting | b. | straight-ticket voting | c. | newly registered
voters | d. | campaigning for party candidates |
|
|
|
38.
|
The functions of the major parties in United States politics include
a. | nominating candidates for office. | b. | insuring the good performance of their elected
candidates. | c. | providing a mechanism for the conduct of government. | d. | all of the
above. |
|
|
|
39.
|
A one-party system
a. | is what the United States has today. | b. | creates an unstable
government. | c. | exists in nearly all dictatorships today. | d. | results in
democracy. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following groups has tended to support the Democratic party in
recent decades?
a. | the business community | b. | Protestants | c. | union
members | d. | white males |
|
|
|
41.
|
The two major parties have members who take all of the following roles
EXCEPT
a. | party leaders. | b. | loyal party members and
voters. | c. | party independents. | d. | party
officeholders. |
|
|
|
42.
|
An increasing number of Americans today
a. | hold political parties in high regard. | b. | vote a straight party line. | c. | favor mandatory
party membership. | d. | identify with neither political
party. |
|
|
|
INTERPRETING CHARTS
Use the chart to answer the following
questions.
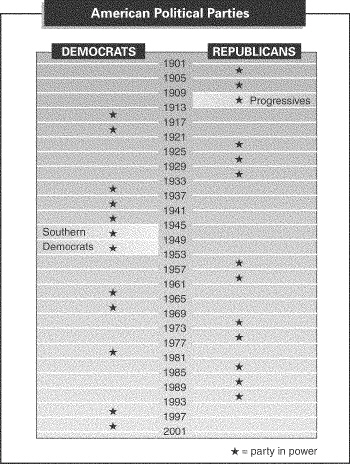
|
|
|
43.
|
Which party was in power during the period 1969–1977?
a. | Progressive | b. | Republican | c. | Southern
Democrat | d. | Democratic |
|
|
|
44.
|
Which year began the shortest period of control by a major party?
|
|
|
45.
|
How many times between 1901 and 1997 did power transfer from Republicans to
Democrats?
|
|
|
46.
|
Which party was in power during the period of 1961–1969?
a. | Progressive | b. | Democratic | c. | Southern
Democratic | d. | Republican |
|
|
|
47.
|
If the main term associated with the Supreme Court is
“Constitution,” then the main term associated with political parties is
a. | “Congress.” | b. | “federalism.” | c. | “elections.” | d. | “Constitution.” |
|
|
|
48.
|
Which of the following do political parties and the news media have in
common?
a. | Both try to inform, inspire, and activate the people with regard to public
affairs. | b. | Both play a major role in deciding the constitutionality of acts of
Congress. | c. | Neither play a role in nominating candidates for public office. | d. | Neither serve to
foster democratic ideals. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which of the following is NOT a reason why the United States has a two-party
system?
a. | Because that is the way it has always been. | b. | Because the
two-party system is established in the Constitution. | c. | Because American election law is written to
discourage minor parties. | d. | Because Americans share many of the same ideals
and principles. |
|
|
|
50.
|
The major difference between a one-party system in a dictatorship and the
modified one-party system found in many States is that
a. | Political parties in a dictatorship offer voters more choices than do those in the
States. | b. | Choice is non-existent in the former, but alive and well in the
latter. | c. | Unlike the States, a dictatorship usually starts with a multiparty system then
narrows the choices to one party. | d. | None of the
above. |
|
|
|
51.
|
Both major parties try to
a. | form a coalition with high-ranking members of Congress. | b. | encourage minor
party candidates. | c. | distance themselves from public policy
issues. | d. | appeal to as many voters as possible. |
|
|
|
52.
|
When trying to predict how an individual will vote, the one factor that is an
accurate indicator more often than any other is
a. | religion. | b. | major events. | c. | family. | d. | economic
status. |
|
|
|
53.
|
During the era of the Democrats that lasted from 1800 to 1860, it can be assumed
that most Americans favored
a. | a government dominated by the President. | b. | a government that
favored the “common people.” | c. | a liberal interpretation of the
Constitution. | d. | tax breaks for big businesses. |
|
|
|
54.
|
Beginning with the Civil War, _____ shifted their support to the Republican
Party.
a. | bankers | b. | southerners | c. | farmers | d. | industrialists |
|
|
|
55.
|
Had Theodore Roosevelt not run for President in the election of 1912, it is
likely that
a. | the Democrats would have won the election. | b. | the incumbent would
have been defeated. | c. | Woodrow Wilson would not have captured the
White House. | d. | Woodrow Wilson would not have lost the election. |
|
|
|
56.
|
Which of the following did NOT contribute to a shift in power from the Democrats
to the Republicans over the course of the nation’s history?
a. | a war | b. | an economic depression | c. | divided
government | d. | a constitutional amendment |
|
|
|
57.
|
If inflation is low, jobs are plentiful, and the Republicans and Democrats each
enjoy strong support, which type of minor party would be LEAST likely to attract voters?
a. | economic protest parties | b. | ideological parties | c. | single-issue
parties | d. | splinter parties |
|
|
|
58.
|
A major party might support a minor party candidate for President if
a. | the major party holds a narrow lead in the polls. | b. | the minor party
candidate is likely to draw votes from the opposition. | c. | the election is too close to
call. | d. | they can borrow from the minor party’s
platform. |
|
|
|
59.
|
The only time both parties have a strong leader at the same time is
a. | between national conventions. | b. | during the nominating
process. | c. | when the party’s presidential candidate has been chosen but before the election
takes place. | d. | after the election but before the new President takes
office. |
|
|
|
60.
|
It can be argued that political parties are at their weakest
a. | when they cannot agree on who to nominate as their candidate. | b. | during the national
convention. | c. | when their candidate is elected President. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
61.
|
Recent laws regulating how political parties fund campaigns have contributed
to
a. | a modified one-party system. | b. | the weakening of the party
system. | c. | the growth of minor parties. | d. | the increased importance of the national
committee. |
|