|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | resolution | b. | rider | c. | discharge petition | d. | quorum | e. | party caucus | f. | filibuster |
|
|
|
1.
|
voted on by either house, but has no force of law
|
|
|
2.
|
closed meeting of the members of each party in the House
|
|
|
3.
|
provision attached to an important bill
|
|
|
4.
|
majority of the full membership of either house
|
|
|
5.
|
enables members to force a bill that has been in committee for 30 days onto the
floor for consideration
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
6.
|
The duties of the House Rules Committee are best described as those of a
a. | factory foreman. | b. | traffic cop. | c. | congressional
chaplain. | d. | accounting clerk. |
|
|
|
7.
|
When the Senate's Republican caucus wants party members to vote for a bill,
the person who determines how many votes can be counted on is the
a. | senior senator. | b. | policy-committee
chairperson. | c. | floor leader. | d. | whip. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The main reason that Congress creates committees is to
a. | divide the workload. | b. | educate new members. | c. | introduce new
bills. | d. | create party power bases. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following is a way a bill can become a law without the
President's signature?
a. | The President delegates the signing of a bill to the Vice
President. | b. | The President waits until the Congress is not in session. | c. | The President fails
to act on the bill within 10 days of receiving it while Congress is in session. | d. | The President leaves
the country. |
|
|
|
10.
|
To propose a constitutional amendment, Congress uses a
a. | public bill. | b. | joint resolution. | c. | concurrent
resolution. | d. | rider. |
|
|
|
11.
|
How and when bills reach the floor of the House is decided by the
a. | Ways and Means Committee. | b. | Rules Committee. | c. | Appropriations
Committee. | d. | Judiciary Committee. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Committee chairpersons usually are chosen
a. | by the presiding officers. | b. | by the whips. | c. | on the basis of
ability. | d. | on the basis of seniority. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Unlike the House, the Senate has a legislative process with
a. | few limits on debate. | b. | strict limits on debate. | c. | no roll-call
voting. | d. | no voice voting. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Bills are introduced in the Senate by
a. | the Rules Committee. | b. | individual senators. | c. | investigative
committees. | d. | the majority floor leader. |
|
|
|
15.
|
In the Vice President's absence, the presiding officer of the Senate is
the
a. | Dean of the Senate. | b. | majority floor leader. | c. | president pro
tempore. | d. | Speaker of the Senate. |
|
|
|
16.
|
The House Rules Committee may do all of the following EXCEPT
a. | set conditions for considering a bill. | b. | speed up consideration of a
bill. | c. | prevent consideration of a bill. | d. | attach amendments to a
bill. |
|
|
|
17.
|
The main way to end a filibuster is by
a. | a two-thirds vote of the Senate. | b. | invoking the Cloture Rule. | c. | convening a
conference committee. | d. | voting the filibusterer out of
office. |
|
|
|
18.
|
On the first day of each new term, the House
a. | has a short, routine day. | b. | has few members to swear
in. | c. | elects a Speaker to preside. | d. | writes all new rules of
procedure. |
|
|
|
19.
|
In order to prevent a bill passed by Congress from becoming law, the President
may
a. | sign it and attach a veto message. | b. | refuse to sign it and attach a veto
message. | c. | sign it after ten days if Congress is in session. | d. | negotiate a
compromise bill with Congress. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Proposed measures that apply to specific individuals or places are
a. | public bills. | b. | private bills. | c. | concurrent
resolutions. | d. | riders. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The president pro tempore
a. | is elected by the House and is the leader of its minority party. | b. | is replaced, when
absent, by the Speaker of the House. | c. | serves in the absence of the Vice President of
the United States. | d. | serves in the absence of the Speaker of the
Senate. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Most select committees do NOT
a. | conduct investigations. | b. | have a specific purpose. | c. | try to bring public
attention to a matter. | d. | produce compromise
bills. |
|
|
|
23.
|
When a bill is introduced in the House, it is FIRST
a. | given to the Rules Committee. | b. | read aloud in full. | c. | given a number and
title. | d. | debated by the full House. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Most measures introduced in the House die at which of these steps?
a. | committee | b. | cloture | c. | quorum | d. | floor vote |
|
|
|
25.
|
The Cloture Rule was adopted following a filibuster over the
a. | arming of American merchant vessels. | b. | passage of the Civil Rights
Act. | c. | stock market crash of the 1920s. | d. | United States’ entry into World War
II. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Conference committees act as a "third house of Congress" when
they
a. | use investigative powers similar to those of the House and
Senate. | b. | screen, debate, and vote on bills. | c. | appoint presiding officers. | d. | produce a compromise
bill that both the House and Senate will accept. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following options is NOT available to a President who has just
received a bill passed by Congress?
a. | sign the bill within 10 days | b. | sign the bill after 15 days | c. | veto the
bill | d. | use a pocket veto |
|
|
|
28.
|
At the beginning of each new term, the Senate
a. | elects a presiding officer. | b. | adopts rules of procedure. | c. | elects a clerk and a
chaplain. | d. | faces few organizational problems. |
|
|
|
29.
|
Majority floor leaders hold considerable power due mainly to the fact
that
a. | they are the most popular leaders. | b. | presiding officers choose
them. | c. | the majority party has more seats than the other party has. | d. | they are assisted by
a powerful whip. |
|
|
|
30.
|
The role of the House Rules Committee is played in the Senate by the
a. | president pro tempore. | b. | president of the Senate. | c. | whip. | d. | majority floor
leader. |
|
|
|
31.
|
In both houses, the standing committees
a. | are always subject-matter committees. | b. | are usually headed by members chosen on the
basis of seniority. | c. | must report out every bill that is referred to
them. | d. | are set up for a limited time to investigate a current
matter. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Bills that originate in either house of Congress may be
a. | introduced only by party leaders. | b. | formulated by private
citizens. | c. | introduced by private citizens. | d. | introduced by the
President. |
|
|
|
33.
|
The purpose of a filibuster is to
a. | invoke the rule of cloture. | b. | prevent quorum calls. | c. | speed up action on a
bill. | d. | prevent action on a bill. |
|
|
|
34.
|
House leaders may use any of these calendars to schedule debate on a bill
EXCEPT
a. | Union Calendar. | b. | House Calendar. | c. | Congressional
Calendar. | d. | Private Calendar. |
|
|
|
35.
|
A compromise bill worked on by a conference committee of House and Senate
members is
a. | usually passed by both houses of Congress. | b. | never passed by both
houses of Congress. | c. | always passed with
amendments. | d. | sometimes passed with amendments. |
|
|
|
INTERPRETING CHARTS
Use the chart to answer the following
questions.
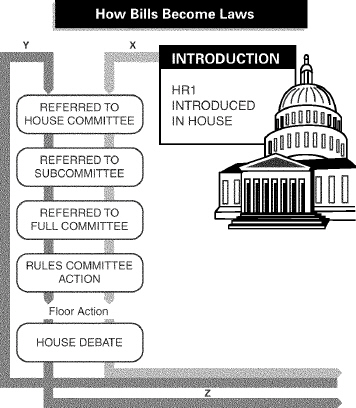
|
|
|
36.
|
To which of the following does a subcommittee report a bill?
a. | the Rules Committee | b. | a conference committee | c. | a full
committee | d. | floor action |
|
|
|
37.
|
A bill traveling along the arrow labeled Z would most likely be headed to
a. | the House. | b. | the Senate. | c. | a joint
committee. | d. | the Supreme Court. |
|
|
|
38.
|
To which of the following does a full committee of the House report a
bill?
a. | a subcommittee | b. | the Rules Committee | c. | a conference
committee | d. | floor action |
|
|
|
39.
|
The arrow labeled X shows that some bills start in the House. Where would
bills traveling along the arrow labeled Y have started from?
a. | pressure groups | b. | the Supreme Court | c. | private
citizens | d. | the Senate |
|
|
|
40.
|
One difference between opening day in the House and opening day in the Senate is
that
a. | new members must be sworn in in the Senate. | b. | committee members
are appointed in the House. | c. | the House must reorganize but not the
Senate. | d. | the Senate reorganizes, but not the House. |
|
|
|
41.
|
The President’s State of the Union message is
a. | an unwritten custom. | b. | a constitutional command. | c. | a personal choice by
each President. | d. | delivered only when Congress issues an invitation to the President to do
so. |
|
|
|
42.
|
In his leadership position, the Speaker must tend not only to the House as a
whole, but also to
a. | his party in particular. | b. | the Senate. | c. | the Congress as a
whole. | d. | the Vice President. |
|
|
|
43.
|
Should the seniority rule be eliminated, which of the following is MOST likely
to gain greater influence over the process of selecting committee chairs?
a. | the voters | b. | the party caucus | c. | the
President | d. | younger members |
|
|
|
44.
|
Because the fate of most bills is decided in committee, it is important for
committee members to
a. | consult party leadership before voting. | b. | call a special
session whenever necessary. | c. | be in touch with current public
opinion. | d. | avoid the input of interest groups. |
|
|
|
45.
|
In each congressional election, a great deal of attention is paid to which party
holds a majority in each chamber. This is at least partly because
a. | the same party is likely to win the presidency. | b. | the majority party
holds a majority of seats on each standing committee. | c. | the Constitution requires each party to hold a
majority at least once in every 10-year period. | d. | State legislatures will likely follow
suit. |
|
|
|
46.
|
The House Rules Committee comes into play
a. | before bills are sent to committee. | b. | while bills are being considered in
committee. | c. | after bills are reported out of committee. | d. | after bills are
considered on the floor. |
|
|
|
47.
|
All of the following describe select committees EXCEPT
a. | their work is usually done in secret. | b. | their members are appointed, not
elected. | c. | they are formed to investigate some specific matter. | d. | most are set up for
a limited time. |
|
|
|
48.
|
Only _____ can propose a measure dealing with raising money.
a. | the Senate | b. | the House | c. | the
voters | d. | the Speaker |
|
|
|
49.
|
One possible reason that a discharge petition is seldom successful is
that
a. | committees rarely pigeonhole a bill. | b. | it can be used only for bills that deal with
financial matters. | c. | it can be used only for concurrent
resolutions. | d. | so many signatures are needed on the discharge
motion. |
|
|
|
50.
|
All of the following are ways the House speeds up the lawmaking process
EXCEPT
a. | making a motion to “move the previous question.” | b. | suspending its
rules. | c. | considering bills as the Committee of the Whole. | d. | opening debate on a
bill. |
|
|
|
51.
|
If the lawmaking process is compared to an obstacle course, which of the
following would constitute an obstacle?
a. | the three readings | b. | being referred to the appropriate standing
committee | c. | being reported out of committee favorably | d. | being
engrossed |
|
|
|
52.
|
Senators may vote to recess rather than adjourn when
a. | they wish to limit discussion of a particular issue. | b. | the end of the
legislative session is nearly at hand. | c. | a member is threatening a
filibuster. | d. | they wish to avoid referring a measure to committee. |
|
|
|
53.
|
The conference committee
a. | is the final step before congressional approval of a bill. | b. | holds hearings to
gather information. | c. | operates differently in the House than it does
in the Senate. | d. | may refuse to report a bill. |
|
|
|
54.
|
The President may veto a bill, but if he does, he must
a. | do so within five days. | b. | give his reasons for doing
so. | c. | return the bill to conference committee. | d. | none of the
above. |
|
|
|
55.
|
List the steps by which a bill becomes a
law....
1-
2-
3-
etc.
|