Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY
TERMS
Match each item with
the correct statement below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than
once. a. | block
grant | b. | concurrent powers | c. | exclusive powers | d. | revenue sharing | e. | reserved powers |
|
|
|
1.
|
those powers exercised solely
by the National Government
|
|
|
2.
|
federal aid given to States
and local governments with virtually no conditions attached
|
|
|
3.
|
those powers not denied to the
States, and not granted specifically to the National Government by the
Constitution
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY
TERMS
Match each item with
the correct statement below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than
once. a. | enabling
act | b. | delegated powers | c. | division of powers | d. | exclusive powers | e. | Privileges and Immunities
Clause |
|
|
|
4.
|
the separation of governmental
powers between the National Government and the 50 State governments
|
|
|
5.
|
those powers granted in the
Constitution only to the National Government
|
|
|
6.
|
provides that a State cannot
take unfair advantage in its laws of the residents of another State
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY
TERMS
Match each item with
the correct statement below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than
once. a. | act of
admission | b. | extradition | c. | grants-in-aid program | d. | inherent powers | e. | enabling act | f. | Privileges and Immunities
Clause |
|
|
|
7.
|
In order for a new State to be
admitted to the Union, Congress must pass a(n) ____ after a State constitution has been approved by
the people of the proposed State.
|
|
|
8.
|
States may receive grants of
federal land under a(n) ____ for such purposes as establishing schools and
colleges.
|
|
|
9.
|
Congress must pass a(n) ____
before a territory can write a proposed State constitution.
|
|
|
10.
|
According to the ____, a State
cannot take unfair advantage in its laws of the residents of another State.
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY
TERMS
Match each item with
the correct statement below. You will not use all the terms. Some terms may be used more than
once. a. | act of
admission | b. | delegated powers | c. | enabling act | d. | reserved powers |
|
|
|
11.
|
A territory seeking Statehood
is first directed to prepare a State constitution by means of a(n) ____.
|
|
|
12.
|
The National Government has
three types of ____ that have been granted to it in the Constitution.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that
best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN
IDEAS
|
|
|
13.
|
The system of federalism
provides for all of the following EXCEPT
a. | local action in matters of local
concern. | b. | a dual system of government. | c. | uniform laws among the
States. | d. | strength through unity. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Concurrent powers are those
that are
a. | exercised simultaneously by the
National and the State governments. | b. | exercised by State governments alone. | c. | exercised by the National Government
alone. | d. | denied to both the National and the State
governments. |
|
|
|
15.
|
An enabling act directs any
area desiring Statehood to
a. | prepare a
constitution. | b. | become an organized territory. | c. | give up its territory. | d. | submit the act to a popular
vote. |
|
|
|
16.
|
States must honor the legality
of one another's civil laws because of the
a. | Necessary and Proper
Clause. | b. | Full Faith and Credit Clause. | c. | Supremacy Clause. | d. | Interstate Compacts
Clause. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Local governments derive their
power from
a. | the Constitution and federal
laws. | b. | State constitutions and State laws. | c. | both State constitutions and the National
Government. | d. | city and county governments. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following is an
expressed power of the National Government?
a. | the power to coin
money | b. | the power to license doctors | c. | the power to acquire
territory | d. | the power to grant divorces |
|
|
|
19.
|
Citizens who commit a crime in
one State and then flee to another State to escape prosecution are to be returned to the original
State under
a. | the Full Faith and Credit
Clause. | b. | the Privileges and Immunities Clause. | c. | extradition. | d. | any interstate compact involving all 50
States. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The Constitution requires the
National Government to guarantee
a. | block grants to every
State. | b. | schools for every community. | c. | an equal number of representatives for every
State. | d. | a republican form of government for every
State. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The power of the National
Government to coin money is
a. | an implied
power. | b. | an inherent power. | c. | an expressed power. | d. | a concurrent
power. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which of the following powers
can the National Government legally exercise?
a. | expressed powers
only | b. | expressed, implied and inherent powers | c. | delegated and reserved
powers | d. | powers not granted to the States |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following is NOT
among the obligations that the National Government has to the States?
a. | protection against foreign attack
and domestic violence | b. | guarantee of a representative form of
government | c. | recognition of each State's legal existence and physical
boundaries | d. | recognition of State constitutions as the supreme law of the
land |
|
|
|
24.
|
From the States' point of
view, what advantage did revenue sharing have over federal grants-in-aid
programs?
a. | establishment of land-grant
colleges | b. | few restrictions on how money could be spent | c. | federal control over policy
matters | d. | FBI expertise and assistance |
|
|
|
25.
|
Agreements States enter into
with both foreign nations and other States with the consent of Congress are
a. | interstate
compacts. | b. | acts of admission. | c. | extraditions. | d. | enabling
acts. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following is the
basic characteristic of federalism?
a. | It divides power between a National
Government and State governments. | b. | It gives most power to the National
Government. | c. | It gives most power to local units of
government. | d. | It encourages citizen participation in
government. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which statement about local
government is accurate?
a. | Local government has no relationship
with State governments. | b. | Local government is an extension of the federal
government. | c. | Local government is a subunit of State
government. | d. | Local government supercedes the authority of State
government. |
|
|
|
28.
|
In the case of
McCulloch v. Maryland,
what was the Supreme Court ruling based upon?
a. | reserved
powers | b. | Full Faith and Credit Clause | c. | Supremacy Clause | d. | interstate
compacts |
|
|
|
29.
|
The Full Faith and Credit
Clause of the Constitution provides that
a. | Congress may not pass laws that
conflict with State laws. | b. | State laws must be uniform. | c. | State laws and court decisions must generally be honored
by other States. | d. | agreements made between the States must first be approved by
Congress. |
|
|
|
30.
|
Funds given to a State by the
National Government with special conditions attached are examples of
a. | block
grants. | b. | revenue sharing. | c. | categorical grants. | d. | project
grants. |
|
|
|
INTERPRETING
DIAGRAMS
Use the diagram to
answer the following questions.
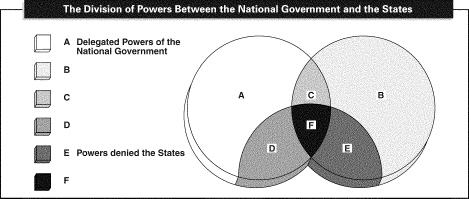
|
|
|
31.
|
What label should appear at the
place marked by the letter D?
a. | Concurrent
Powers | b. | Powers reserved to the States | c. | Powers denied both the National Government and the
States | d. | Powers denied the National
Government |
|
|
|
32.
|
What label should appear at the
place marked by the letter B?
a. | Concurrent
Powers | b. | Powers denied the National Government | c. | Powers reserved to the
States | d. | Powers denied both the National Government and the
States |
|
|
|
33.
|
What label should appear at the
place marked by the letter C?
a. | Concurrent
Powers | b. | Powers denied the National Government | c. | Powers reserved to the
States | d. | Powers denied both the National Government and the
States |
|
|
|
34.
|
What label should appear at the
place marked by the letter F?
a. | Concurrent
Powers | b. | Powers reserved to the States | c. | Powers denied both the National Government and the
States | d. | Powers denied the National
Government |
|
|
|
35.
|
The label Powers reserved to the States belongs at the place
marked by
a. | the letter F. | b. | the letter B. | c. | the letter C. | d. | the letter D. |
|
|
|
36.
|
The label Powers denied to the National Government should be
placed at
a. | the letter E. | b. | the letters D and B. | c. | the letters C and F. | d. | the letter D. |
|
|
|
37.
|
The Framers limited the power
of the National Government both by creating separate branches and by
a. | giving some powers only to the
States. | b. | giving the National Government only the expressed
powers. | c. | providing for formal amendment to the
Constitution. | d. | both b and c |
|
|
|
38.
|
Without the expressed powers of
the National Government, there would be no
a. | division of
power. | b. | reserved powers. | c. | implied powers. | d. | inherent powers. |
|
|
|
39.
|
State governments can claim
no
a. | powers belonging to local
governments. | b. | inherent powers. | c. | concurrent powers. | d. | reserved
powers. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following
statements about the powers of the National Government is TRUE?
a. | It is a government of delegated
powers. | b. | The Elastic Clause limits those powers. | c. | Each of the inherent powers must be traceable to some
expressed power. | d. | Only the Congress exercises the expressed
powers. |
|
|
|
41.
|
Through which of the following
are the States denied powers?
a. | the Constitution of the United
States | b. | inherently, through the existence of the federal
system | c. | the individual State constitutions | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which of the following BEST
describes this statement: “The States are actually the most important players in the federal
system.”
a. | fact | b. | opinion | c. | constitutional provision | d. | both a and c |
|
|
|
43.
|
Which of the following may have
led the Framers to include the Supremacy Clause in the Constitution?
a. | conflicts among the States during
the Critical Period | b. | the writings of John Locke | c. | the example set by the State
constitutions | d. | the Court’s ruling in McCulloch v. Maryland |
|
|
|
44.
|
Judging by the actions of
Congress after the Civil War, a “republican form of government” must
allow
a. | a State to leave the
Union. | b. | a federal system. | c. | equal rights to all citizens. | d. | formal amendments to the
Constitution. |
|
|
|
45.
|
The obligation of the National
Government to protect the States against invasion indirectly arose because the new
Constitution
a. | established a federal
system. | b. | required the States to give up their war-making
powers. | c. | forbid State militias. | d. | denied all powers to the
States. |
|
|
|
46.
|
States gain needed resources
through grants-in-aid, while the National Government gains
a. | needed
funds. | b. | statistical data. | c. | influence over State and local affairs. | d. | assistance with public
works. |
|
|
|
47.
|
The power of the Federal
Government to make grants-in-aid can be traced to which expressed power of
Congress?
a. | the power to admit new
States | b. | the power to coin money | c. | the power to regulate
commerce | d. | the power to lay and collect
taxes |
|
|
|
48.
|
Since the Reagan administration
converted many categorical grants into block grants, which of the following statements about that
administration is most likely to be true?
a. | The Reagan administration tried to
reduce the role played by the Federal Government in State and local
matters. | b. | The Reagan administration tried to reduce the federal
budget. | c. | The Reagan administration tried to increase the role played by the Federal
Government in State and local matters. | d. | The Reagan administration wanted grant monies to be earmarked for specific
projects. |
|
|
|
49.
|
In which of the following
situations would one State NOT give full faith and credit to the public acts of another
State?
a. | a man convicted of burglary in
Wisconsin moves to Utah | b. | a resident of Nevada obtains a divorce then moves to
Montana | c. | a woman married in Oklahoma needs to prove her marital status for a new job in
Florida | d. | a person born in Pennsylvania wishes to obtain a driver’s license in
Vermont |
|
|
|
50.
|
In certain situations, States
can give preferential treatment to _____ over ______.
a. | nonresidents/residents | b. | residents/nonresidents | c. | fugitives/divorcees | d. | civil matters/criminal
matters |
|
|
|
51.
|
Just as treaties made by the
President are subject to consent by the Senate, interstate compacts are subject
to
a. | judicial
review. | b. | presidential consent. | c. | review by the States not involved in the
compact. | d. | congressional consent. |
|